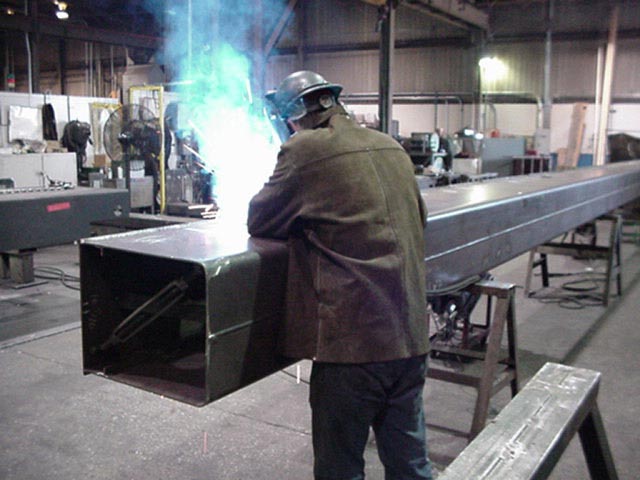
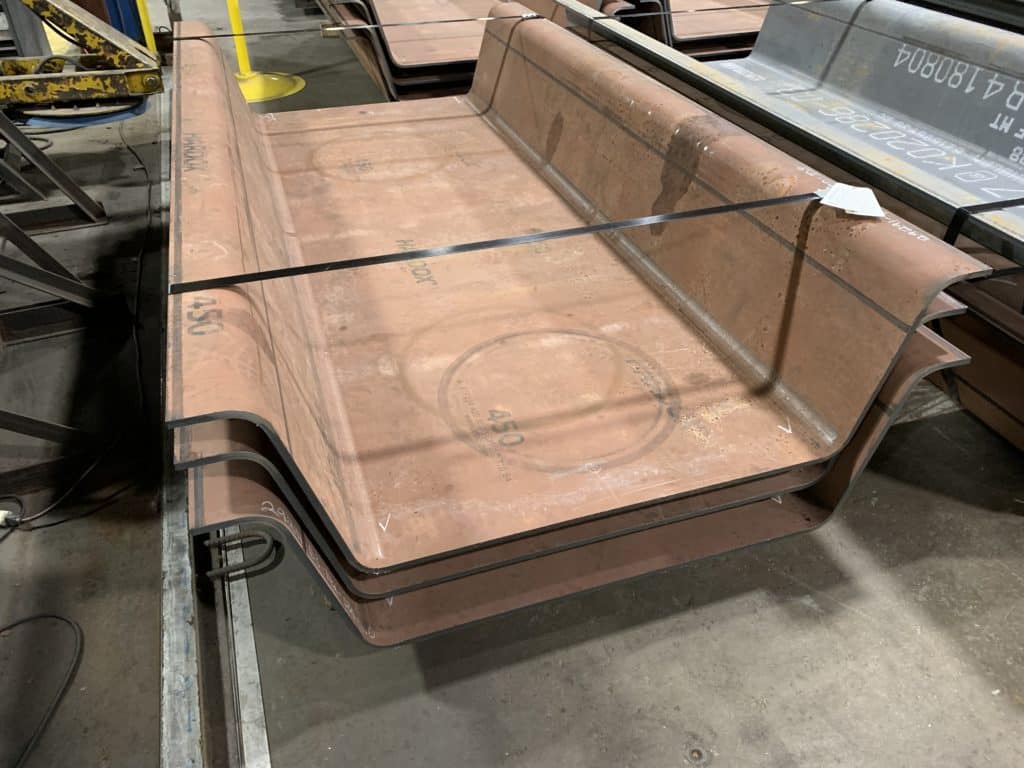
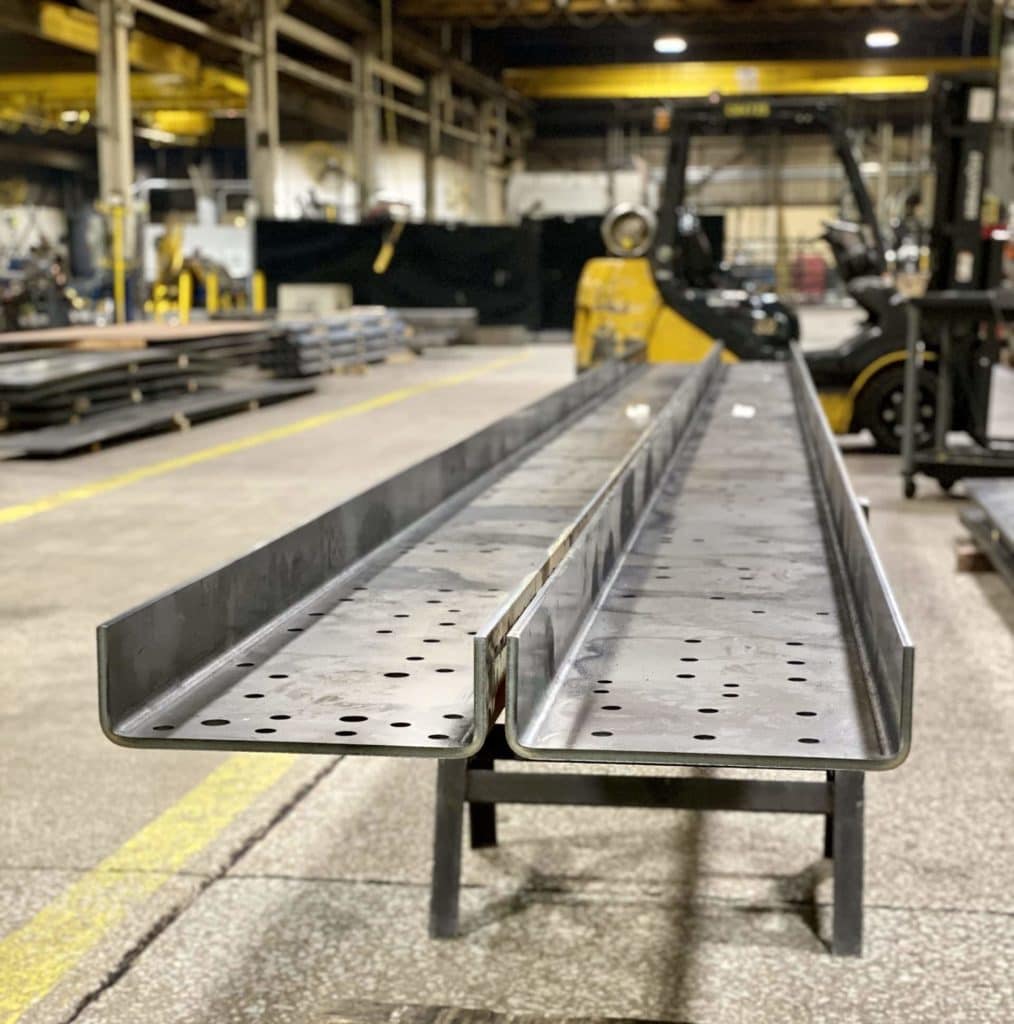
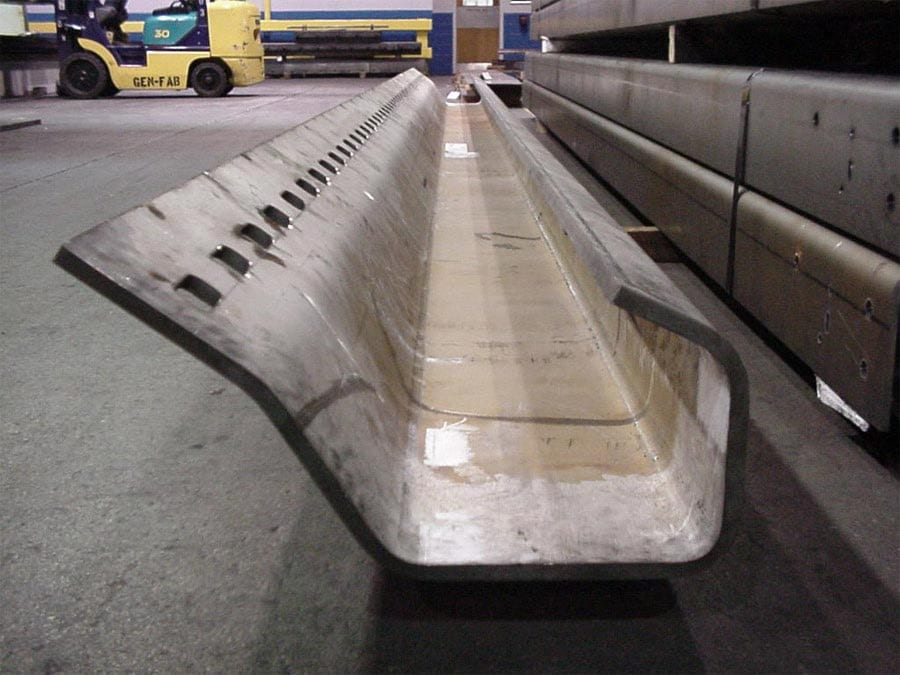
At G.E. Mathis Company, our precision computer numerical control (CNC) plasma cutting capabilities allow us to produce unmatched quality components.
We provide CNC high-definition plasma cutting services using 400-amp dual-head 4-axis equipment. Our cutting table is 10 feet wide by 90 feet long and can produce various components up to three inches thick while holding some of the tightest tolerances in the industry. We can plasma cut numerous materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, high-strength steel, abrasion-resistant (AR) steel such as HARDOX®, high-strength low alloy steels such as STRENX®, and other alloys.
Our CNC high-definition plasma cutting capabilities have served various markets and industries, including agriculture, construction/cranes, mining, aerospace, energy, trailers/truck bodies, and military. We also have experience manufacturing components for diverse applications, such as boom components, frame rails, lifting equipment, truck cranes, wear parts, and more. Simply put, there are few projects our plasma cutting capabilities cannot undertake.
Our typical lead times may be as short as 1-2 weeks, depending on the project’s details.
Precision CNC high-definition Plasma Cutting
Gas begins to ionize when subjected to extreme heat. This ionized gas then becomes plasma, a more electrically conductive state of matter. The plasma cutting process harnesses plasma’s conductive properties to cut conductive materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
The Plasma Cutting Process
A plasma cutting machine consists of several components:
- A plasma power supply capable of generating 200-400 volts of direct current, which powers the plasma arc responsible for ionizing the gas and regulates the power output based on the material’s type and thickness
- An arc-starting console capable of producing 5,000 volts of alternating current at 2 MHz to generate the spark inside the torch that creates the plasma arc
- A plasma torch through which ionized gas passes
When combined with the gas, the arc from the power supply results in a plasma jet reaching a maximum temperature of 40,000°F. This jet then passes through an alloy copper nozzle, allowing the torch to cut through any conductive material.
The plasma torch itself entails the following components:
- An electrode connected to the negative side of the power supply
- A nozzle connected to the positive side of the power supply
- A gas baffle used to swirl the gas
The actual cutting process begins by sending a start input to the plasma system. After starting the power supply, the system places a negative voltage on the electrode located within the plasma torch. The gas then begins to flow to the torch while the baffle begins to swirl it.
During plasma cutting, swirling the gas provides maximum cutting efficiency and quality. Facilitating swirling typically involves injecting water where the arc exits the nozzle, further constricting the arc. The temperature of the water used to swirl the gas should not exceed 70°F.
Closing the nozzles in the next stage of the process allows the gas to connect to the power supply’s positive side. A high-frequency generator then causes a spark to pass between the nozzle and electrode, ionizing the gas. The pilot arc begins to flow between the electrode and nozzle, the gas flow blows the arc out of the nozzle, and the pilot arc makes contact with the material to be cut. After the main arc increases power to the cutting amperage, the shield gas restricts the plasma arc to ensure a neat cut.
Advantages of Plasma Cutting
CNC plasma cutting has significant advantages over alternative cutting methods. Some of these benefits include:
- Better cut quality
- The ability to cut through thick steel, aluminum, and other metals
- Fast cutting speeds
- Minimal risk of warping
Typical Materials Used in Plasma Cutting Operations
The plasma cutting process accommodates a wide range of conductive materials. However, two of the materials most commonly used in plasma cutting operations include stainless steel and aluminum.
Overview of Stainless Steel Plasma Cutting Operations
Plasma cutting and stainless steel have gone hand-in-hand for decades. Still, recent advancements in plasma cutting techniques and technologies have led to significant improvements in the quality of plasma-cut stainless steel parts and products. For example, modern plasma cutting systems offer a broader selection of cutting gases and amperages, allowing machine operators to choose the cutting option that best suits the specific grade and thickness of the stainless steel workpiece. As a result, they can achieve greater cutting precision and better cutting quality, both of which translate to lower overall production costs.
Overview of Aluminum Plasma Cutting Operations
Like stainless steel, improvements in plasma cutting techniques and technologies have made the plasma cutting process an effective and affordable manufacturing method for aluminum parts and products. Modern plasma cutting allows manufacturers to create precise angles and curves in aluminum sheets and plates of varying thicknesses (up to six inches). However, the success of the project depends on whether they use the right equipment and settings. For example, high-powered, computer-controlled plasma torches can cut aluminum plates up to 150 millimeters in thickness when correctly configured.
Contact the Plasma Cutting Experts at G.E. Mathis Company Today
Headquartered in Chicago, G.E. Mathis Company is proud to offer CNC plasma cutting services to customers in every industry, as well as precision laser processing, press-brake forming, and welding. Throughout our 119 years in business, we’ve worked with a wide range of materials. This insight allows us to identify the proper cutting techniques and technologies for each material.
We are happy to assist customers in identifying the best cutting process for a material. For additional information on our precision CNC plasma cutting services, click to expand the tables below.
Through more than a century of business, G.E. Mathis Company has remained committed to our customers. Our AWS-D1.1 and ISO 9001:2015 certifications give our customers peace of mind, knowing they will always receive the best products and services when they choose G.E. Mathis Company.
We also provide the following support services to help our customers with sustainability and traceability initiatives:
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) – All Levels
- First Article Inspection Report (FAIR)
- Capability Studies (Statistical Process Control)
- Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT)
To learn more about our company and our metal forming capabilities, or to discuss an upcoming project, please contact us today. We look forward to working with you.
Request Quote
Please complete the form below and we will contact you shortly.
Over 100+ Years of Experience
Trained & Certified Expertise
Reliable Customer Service